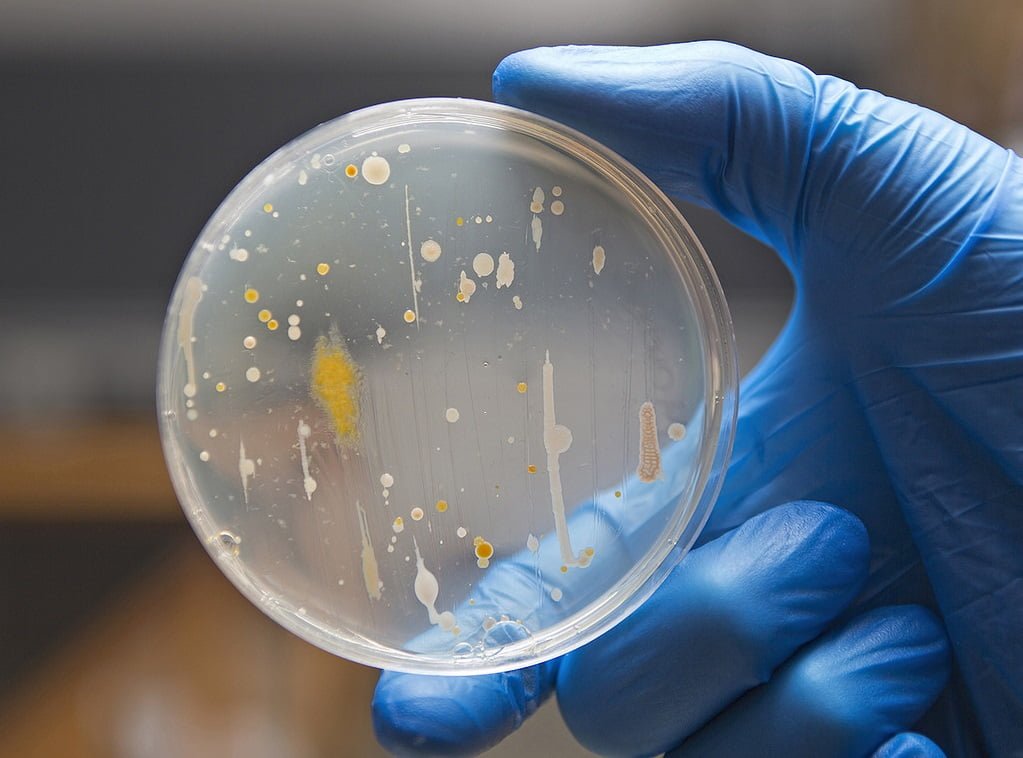
Microbiological purity tests of cosmetics are an important element for the development of the most important document proving the quality of a given product, which is the cosmetic product safety report. On its basis one can conclude on the safety of a given cosmetic product placed on the market by the producer. The requirement to test the microbiological purity of cosmetic products or raw materials intended for their production results directly from the Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council (EC) No. 1223/2009 of November 30, 2009, applicable throughout the European Union.
Risk of contamination of cosmetics
The greatest risk in terms of microbiological contamination is posed by cosmetics with a high water content or based on it. Water in cosmetic products can be a potential source of Pseudomonas bacteria (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa) or Escherichia coli, which are pathogenic microorganisms and therefore their presence in cosmetic products is unacceptable. This is one of the reasons why it is important not only to control the microbiological quality of finished products, but also to periodically test raw materials, such as production water.
Types of microbiological purity test for cosmetics
The overall examination of microbiological purity is influenced by quantitative and qualitative analyzes which focus on the total number of microorganisms. Qualitative analyzes are performed to detect the presence of specific microorganisms, i.e. undesirable mesophilic aerobic bacteria or yeasts that are pathogenic and harmful to human health in cosmetic products, such as: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans.
Methods of testing cosmetics
Different microbiological culture media shall be used to detect the presence of each of the micro-organisms sought. The test procedure is carried out according to the current ISO standards. For example, to detect the presence of Escherichia coli in a product, the bacteria must be cultured on MacConkey’s selective and differential culture medium, on which Escherichia coli will form dark pink colonies with a characteristic dark pink border around them. Baird-Parker’s selective and differential medium is used for the isolation of Staphylococcus aureus cocci. Coagulase-positive staphylococci grown on this medium will have a black color with a characteristic light zone around it. For the detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria, a selective CET (Cetrymide Agar) medium is used, thanks to which characteristic neon yellow-green bacterial colonies will be detected. To check the presence of Candida yeast fungi in the cosmetic product, spread plate method should be performed on a selective medium dedicated to the isolation of Sabouraud fungi with dextrose and chloramphenicol, on which Candida albicans will grow in the form of large, snow-white colonies.
Feel free to contact the Customer Service Office in order to learn more about the detailed offer of cosmetics tests provided by the Ekolabos laboratory +48 22 378 30 34 or kosmetyki@ekolabos.pl
